What are the benefits of upgrading to a new EFTPOS machine?

1 July 2016 - 18 min read
EFTPOS Education

Every business has an obligation to comply with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Find out how you can be compliant.
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a data security standard designed to assist merchants and their service providers in appropriately protecting card data. It is adopted by the major card schemes, including Mastercard® and Visa.
The PCI DSS applies to all businesses. Compliance obligations differ depending on the number of transactions processed and the nature of these transactions.
Each business is assigned a PCI DSS level, which is determined by the number of transactions processed per year and the nature of these transactions. High transacting businesses are considered to be Level 1 and low transacting merchants are considered to be Level 4.
Tyro will seek to determine your PCI DSS level at the time of onboarding, however this level may change over time.
Merchants in levels 1, 2, and 3 have an obligation to attest to their level of compliance on an annual basis and provide periodical updates to Tyro on their compliance activities. There is no requirement for Level 4 merchants to attest to PCI DSS compliance, however there is an obligation for these merchants to comply with the Standard.
Criminals seek to steal card data from one merchant and use this data to commit fraud against other merchants, leading to financial loss for these other merchants and inconvenience for the cardholders whose data has been stolen. These attacks are formally known as Account Data Compromise (ADC) events, or less formally as hacking events, and acquirers are required by the card schemes to investigate these events in order to understand the manner in which card data was stolen and the extent to which card credentials were placed at risk.
By protecting card data, merchants reduce the potential for criminal activity, protect themselves and their customers, and assist in protecting the integrity of the card payments ecosystem.
Compliance with the PCI DSS is a journey and requires ongoing activity and investment.
Level 3 and 4 merchants should start by considering the Prioritised Approach made available by the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) and noted below.
Level 1 and 2 merchants should also consider the Prioritised Approach, however should also engage the services of appropriately qualified security professionals to assist them on their compliance journey.
Non-compliance with the PCI DSS may leave you vulnerable to a hacking event and compromise the good name of your business and the credentials of your customers.
If you are unable to validate compliance with the PCI DSS in an agreed time-frame, whether this requirement relates to your PCI DSS level or actions required to be taken following a hacking event, Tyro may withdraw your merchant facility and this may hamper your efforts to obtain merchant services from another acquirer.
Merchants falling victim to hacking events or failing to validate PCI DSS compliance may also be liable for card scheme fines.
All merchants should take steps to protect card data by ensuring that their systems and those of their service providers, including eCommerce shopping carts, are regularly reviewed for malware and unauthorised access, patched, and virus protected to maintain the integrity of card data being stored, processed, and transmitted.
Tyro recommends that eCommerce merchants avoid storage, processing, and transmission of card data wherever possible, and instead opt for storage of card data in a PCI DSS compliant environment by way of a Hosted Payment Page (HPP).
The Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) describes the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) as “the global standard adopted by the payment card schemes for all entities that process, store or transmit cardholder data and/or sensitive authentication data.” The PCI DSS is supported by major card schemes, including founding members American Express, Discover, JCB, Mastercard, and Visa.
The PCI DSS applies to any entity that accepts or processes payment cards, which importantly includes merchants and their chosen service providers. It consists of six goals and twelve requirements that mirror security best practices, namely:
| Goals | PCI DSS Requirements |
| Build and Maintain a Secure Network and Systems | REQ 1 – Install and maintain a firewall configuration to protect cardholder data
REQ 2 – Do not use vendor-supplied defaults for system passwords and other security parameters |
| Protect Cardholder Data |
REQ 3 – Protect stored cardholder data
REQ 4 – Encrypt transmission of cardholder data across open, public networks |
| Maintain a Vulnerability Management Program |
REQ 5 – Protect all systems against malware and regularly update anti-virus software or programs
REQ 6 – Develop and maintain secure systems and applications |
| Implement Strong Access Control Measures |
REQ 7 – Restrict access to cardholder data by business need to know
REQ 8 – Identify and authenticate access to system components REQ 9 – Restrict physical access to cardholder data |
| Regularly Monitor and Test Networks |
REQ 10 – Track and monitor all access to network resources and cardholder data
REQ 11 – Regularly test security systems and processes |
| Maintain an Information Security Policy | REQ 12 – Maintain a policy that addresses information security for all personnel |
Compliance is an important component of the PCI DSS, however fundamentally this is a data security standard and therefore security of card data is the key objective.
Achievement of PCI DSS compliance is a journey and takes time and effort to realise. For this reason, the PCI SSC provides a Prioritised Approach to help merchants and other organisations incrementally protect against the highest risk factors and escalating threats whilst on the road to PCI DSS compliance: https://www.pcisecuritystandards.org/documents/Prioritized-Approach-for-PCI_DSS-v3_2.pdf
Whilst the PCI SSC sets the standards for the PCI DSS, each card scheme has its own programme for compliance, validation levels and enforcement.
Depending on the characteristics of the merchant, compliance may be achieved by way of the following:
Tyro’s requirements for PCI DSS compliance validation are set-out in the table below and are based upon programs communicated by Mastercard and Visa. Tyro reserves the right to re-classify the compliance level of merchants at any time and for any reason.
| PCI DSS Level | Annual Number of Transactions or Merchant Type | Compliance Validation Requirements | Reporting Requirements | Notes |
| Level 1 |
Merchants processing more than 6 million transactions for any scheme
Payment facilitators |
Every year:
Every quarter:
|
Every six months:
|
Where a merchant is non-complaint with the PCI DSS, the merchant must provide a roadmap to achieving compliance, along with milestones and a target end date. Tyro will report this information to the card schemes on a six-monthly basis. Ultimately the card schemes will determine the acceptability of the roadmap and may levy fines or penalties for non-compliance. The ROC is provided by the QSA/ISA. The AOC is provided by the merchant. |
| Level 2 | Merchants processing more than 1 million and less than 6 million transactions for any scheme |
Every year:
Every quarter:
|
Every six months:
|
Where a merchant is non-complaint with the PCI DSS, the merchant must provide a roadmap to achieving compliance, along with milestones and a target end date. Tyro will report this information to the card schemes on a six-monthly basis. Ultimately the card schemes will determine the acceptability of the roadmap and may levy fines or penalties for non-compliance. The SAQ is provided by the merchant, however can be prepared by the merchant or a QSA/ISA. If provided by the merchant, the SAQ must be signed by a QSA or ISA. The AOC is provided by the merchant. |
| Level 3 | Merchants processing more than 20,000 and less than 1 million eCommerce transactions for any scheme |
Every year:
Every quarter:
|
Every six months:
|
Where a merchant is non-complaint with the PCI DSS, the merchant must provide a roadmap to achieving compliance, along with milestones and a target end date. Tyro will report this information to the card schemes on a six-monthly basis. Ultimately the card schemes will determine the acceptability of the roadmap and may levy fines or penalties for non-compliance. The SAQ is provided by the merchant, however can be prepared by the merchant or a QSA/ISA. The AOC is provided by the merchant. Merchants processing more than 1 million and less than 6 million eCommerce transactions for any scheme are elevated to Level 2 status and are required to engage the services of a QSA or ISA. Where more than 6 million transactions are processed for any scheme, merchants are elevated to Level 1 status and are required to engage the services of a QSA/ISA. |
| Level 4 |
All other merchants (i.e. Merchants processing less than 20,000 eCommerce transactions for any scheme and all other merchants processing up to 1 million transactions for any scheme) |
Unless otherwise required by Tyro, there is no requirement to meet compliance validation requirements, however it is recommended that merchants undertake the following tasks in order to assess their level of security and compliance with the PCI DSS: Every year:
Every quarter:
|
There are no reporting requirements at this time, unless required by Tyro | N/A |
All merchants have an obligation to protect card data and are encouraged to assess their compliance with the PCI DSS. Some merchants are required to validate compliance, as per the table above.
Use of a Tyro Hosted Payment Page (HPP) in an eCommerce context limits the scope of the PCI DSS for merchants, assuming that these HPPs are housed in a PCI DSS compliant environment.
For merchants required to, or opting to, validate compliance using a QSA or ISA, the PCI SSC provides a list of:
The PCI SSC also provides a list of accredited ASVs:
Accredited ASVs: https://listings.pcisecuritystandards.org/assessors_and_solutions/approved_scanning_vendors
For merchants required to, or opting to, validate compliance by way of a SAQ, selection of the appropriate SAQ is an important first step. Different SAQs are applicable to different merchant contexts. Review the diagram below to determine SAQ applicability:

The PCI SSC provides:
An ADC event occurs when a third party gains unauthorised access to card data held in a physical and/or electronic form. Stolen card data may be used to commit fraud, and in Australia this is most common in a card not present context.
ADC events can be detected in different ways, with the most common way being via a Common Point of Purchase (CPP) event. A CPP occurs when card issuers detect abnormal levels of fraud activity on their cards and triangulate this fraud to a common identifier, for example a specific merchant facility. When CPP events are observed, card issuers and/or card schemes will notify Tyro and require steps to be taken depending on the context.
ADC events have broad-ranging impacts on the compromised merchant, cardholders, acquirers, card issuers, and damage the brand and integrity of the card payments ecosystem. Depending on the nature and extent of the ADC, the card schemes may warrant that a forensic investigation is required to identify the cause of the compromise and the amount of card data that has been placed at risk. Once an ADC event has been contained, Tyro will prescribe steps required to be taken by the merchant to achieve PCI DSS compliance and/or allow card processing to re-commence, which may include compliance validation by way of a QSA.
In the event of an ADC event, merchants are advised to:
The PCI SSC provides a list of qualified PCI Forensic Investigators (PFI):
In addition to the PCI DSS that applies to merchants and service providers, other standards apply to device manufacturers and software developers, as shown in the caption below.
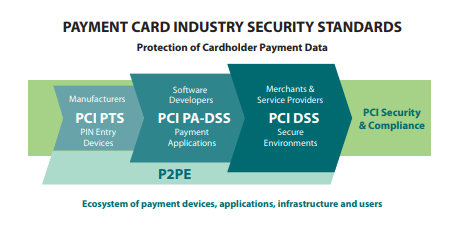
The PCI SSC provides a list of:
The card schemes reserve the right to fine and/or penalise acquirers and/or merchants for non-compliance with the PCI DSS or in the event of an ADC event or series of events. Fines and penalties depend on the specific context.
At the time of onboarding, merchants will be asked to provide an indication as to the number of transactions that will be processed via their merchant facility. Merchants likely to fall into Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 categories will be contacted by Tyro to discuss PCI DSS obligations.
Merchants progressing from Level 4 to other levels will be contacted by Tyro at the appropriate time.
Tyro is required to report to Mastercard and Visa on the compliance status of Level 1, Level 2, Level 3, and ADC merchants on a twice-yearly basis. No reporting is required for Level 4 merchants at this time.
Mastercard reporting is presented in the SDP Acquirer Submission and Compliance Status Form by 31 March and 30 September.
Visa reporting is presented in the Acquirer Merchant Compliance Validation Reporting Template by 31 March and 30 September.
The PCI SSC provides the PCI DSS Quick Reference Guide: https://www.pcisecuritystandards.org/documents/PCIDSS_QRGv3_2.pdf?agreement=true&time=1529025362482
| PCI DSS Level | Annual Number of Transactions or Merchant Type | Compliance Validation Requirements | Reporting Requirements | Notes |
| Level 1 |
Merchants processing more than 6 million transactions for any scheme Payment facilitators |
Every year:
Every quarter:
|
Every six months:
|
Where a merchant is non-complaint with the PCI DSS, the merchant must provide a roadmap to achieving compliance, along with milestones and a target end date. Tyro will report this information to the card schemes on a six-monthly basis. Ultimately the card schemes will determine the acceptability of the roadmap and may levy fines or penalties for non-compliance. The ROC is provided by the QSA/ISA. The AOC is provided by the merchant. |
| Level 2 | Merchants processing more than 1 million and less than 6 million transactions for any scheme |
Every year:
Every quarter:
|
Every six months:
|
Where a merchant is non-complaint with the PCI DSS, the merchant must provide a roadmap to achieving compliance, along with milestones and a target end date. Tyro will report this information to the card schemes on a six-monthly basis. Ultimately the card schemes will determine the acceptability of the roadmap and may levy fines or penalties for non-compliance. The SAQ is provided by the merchant, however can be prepared by the merchant or a QSA/ISA. If provided by the merchant, the SAQ must be signed by a QSA or ISA. The AOC is provided by the merchant. |
| Level 3 | Merchants processing more than 20,000 and less than 1 million eCommerce transactions for any scheme |
Every year:
Every quarter:
|
Every six months:
|
Where a merchant is non-complaint with the PCI DSS, the merchant must provide a roadmap to achieving compliance, along with milestones and a target end date. Tyro will report this information to the card schemes on a six-monthly basis. Ultimately the card schemes will determine the acceptability of the roadmap and may levy fines or penalties for non-compliance. The SAQ is provided by the merchant, however can be prepared by the merchant or a QSA/ISA. The AOC is provided by the merchant. Merchants processing more than 1 million and less than 6 million eCommerce transactions for any scheme are elevated to Level 2 status and are required to engage the services of a QSA or ISA. Where more than 6 million transactions are processed for any scheme, merchants are elevated to Level 1 status and are required to engage the services of a QSA/ISA. |
| Level 4 |
All other merchants (i.e. Merchants processing less than 20,000 eCommerce transactions for any scheme and all other merchants processing up to 1 million transactions for any scheme) |
Unless otherwise required by Tyro, there is no requirement to meet compliance validation requirements, however it is recommended that merchants undertake the following tasks in order to assess their level of security and compliance with the PCI DSS: Every year:
Every quarter:
|
There are no reporting requirements at this time, unless required by Tyro | N/A |
Mastercard is a registered trademark, and the circles design is a trademark of Mastercard International Incorporated.
You may also like
17 Dec 2024 - 2 min read
13 Dec 2024 - 2 min read
12 Dec 2024 - 0 min read
5 Dec 2024 - 2 min read
Australian-based 24/7 support